| Type of Paralysis | Description |
|---|---|
| Monoplegia | Paralysis affecting only one limb (either an arm or a leg). |
| Hemiplegia | Paralysis of one side of the body (right or left), typically after a stroke. |
| Paraplegia | Paralysis of both legs and possibly the lower part of the body. |
| Quadriplegia | Paralysis of all four limbs (arms and legs), often due to spinal cord injury. |
| Facial Paralysis | Affects facial muscles; commonly seen in Bell’s palsy or stroke. |
| Localized Paralysis | Paralysis limited to a specific area, such as the hands, vocal cords, etc. |
| Generalized Paralysis | Widespread paralysis affecting large portions of the body. |
| Spastic Paralysis | Muscles become stiff and tight due to continuous contraction. |
| Flaccid Paralysis | Muscles become soft and limp with loss of tone, often due to nerve damage. |
Bhomeo Homeopathyपैरालिसिस से मुक्त हो जाओ
पैरालिसिस से मुक्त हो जाओ
होम्योपैथी का सहारा अपनाओ
हर चुनौती को गले लगाएं, होम्योपैथी के साथ नई जीत की कहानी लिखें

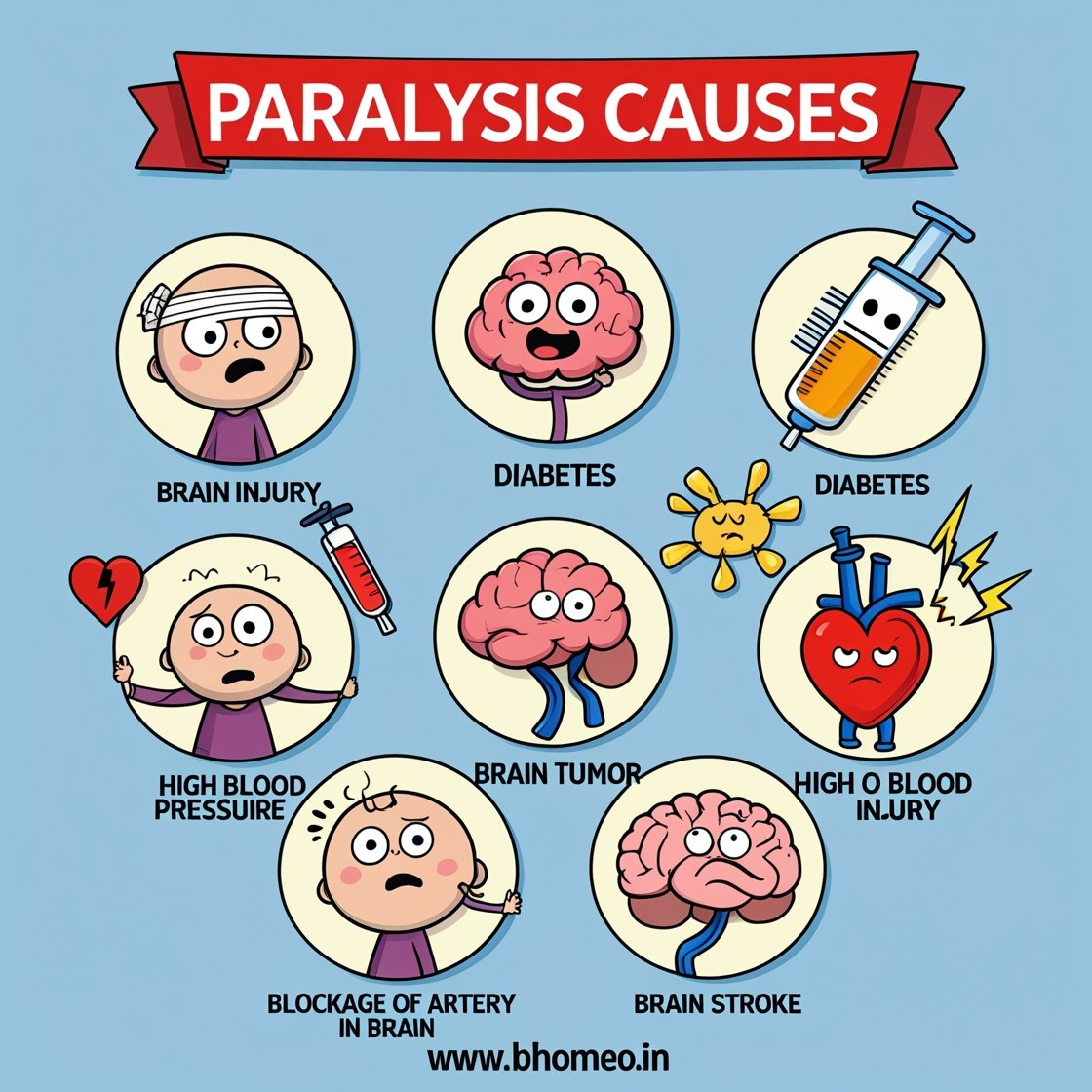
Paralysis - कारण, लक्षण, जाँच, होम्योपैथी इलाज
Paralysis Symptoms, Types, Causes, and Homeopathy Treatment
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Symptoms | – Loss of muscle function in part of the body – Numbness or tingling sensation – Muscle weakness – Loss of coordination or balance – Difficulty speaking or swallowing |
| Types | – Monoplegia: Paralysis of one limb – Hemiplegia: Paralysis of one side of the body – Paraplegia: Paralysis of both legs – Quadriplegia: Paralysis of all four limbs – Facial Paralysis: Affects facial muscles (e.g., Bell’s palsy) |
| Causes | – Stroke – Spinal cord injury – Head trauma – Multiple sclerosis – Cerebral palsy – Infections (e.g., polio) – Tumors – Neurological disorders |
| Homeopathy Treatment | – Causticum: For paralysis with stiffness and muscle contracture – Plumbum Met: For paralysis with muscle atrophy – Gelsemium: For weakness and trembling with paralysis – Lathyrus Sativus: For lower limb paralysis – Conium: For progressive paralysis with vertigo – Nux Vomica: For paralysis due to overexertion or stimulants |
Types Of Paralysis
पेरीफेरल नर्व पॉलीन्यूरोपैथी (Peripheral Neuropathy)
यह स्थिति तब होती है जब तंत्रिका तंतु क्षतिग्रस्त या खराब हो जाते हैं, जिससे हाथ और पैरों में कमजोरी या पैरालिसिस हो सकता है।
स्पाइनल कॉर्ड इंजुरी (Spinal Cord Injury)
रीढ़ की हड्डी में चोट लगने से विभिन्न प्रकार की पैरालिसिस हो सकती है, जैसे कि त्रिगति पैरालिसिस (Tetraplegia) या पक्षाघात (Paraplegia)।
हंटिंग्टन का रोग (Huntington’s Disease)
यह एक आनुवंशिक बीमारी है जो मस्तिष्क की कोशिकाओं को नुकसान पहुंचाती है, जिससे मांसपेशियों में कमजोरी और पैरालिसिस हो सकता है।
गेट्समैन सिंड्रोम (Guillain–Barré Syndrome)
यह एक दुर्लभ ऑटोइम्यून रोग है जिसमें शरीर की प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली गलती से तंत्रिका तंतुओं पर हमला कर देती है, जिससे कमजोरी या पैरालिसिस हो सकता है।
संज्ञात तंत्रिका दोष (Peripheral Nerve Damage)
यह स्थिति आमतौर पर चोट, संक्रमण या तंत्रिकाओं की खराब कार्यप्रणाली के कारण होती है, जिससे मांसपेशियों में कमजोरी या पैरालिसिस हो सकता है।
गैलिएन या संक्रामित तंत्रिका दोष (Poliomyelitis)
यह पोलियो वायरस के संक्रमण से होने वाला रोग है, जो केंद्रीय तंत्रिका तंत्र को प्रभावित करता है। यह रोग विशेष रूप से बच्चों में अधिक होता है और पैरों में लकवा पैदा कर सकता है।
Comman medicine used In Paralysis
Homeopathy takes a holistic approach to treating Paralysis, addressing the root cause rather than just managing the symptoms. Unlike conventional treatments, which often provide temporary relief, homeopathic remedies focus on strengthening the body's natural defenses. Some commonly used homeopathic remedies for Paralysis:
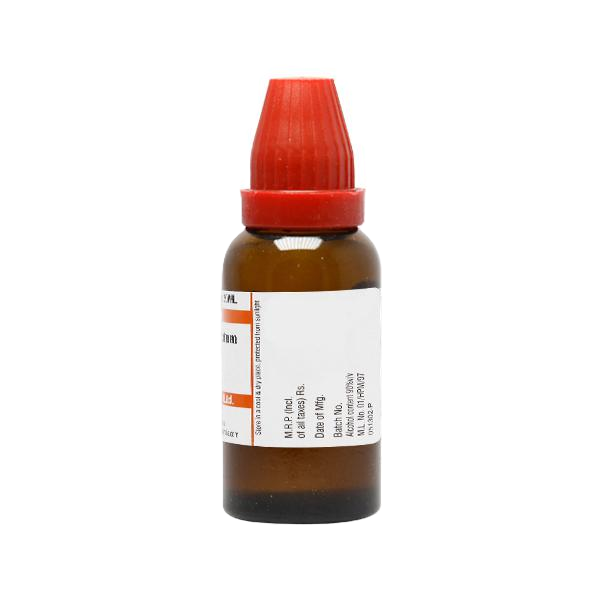
Caust

Rhus-t

Op

Gels
Disclaimer
होम्योपैथी दवाई केवल होम्योपैथी डॉक्टर की सलाह के बाद ही लेनी चाहिए अन्यथा गंभीर दुष्प्रभाव हो सकते हैं
Homeopathy medicine should be taken only after homeopathy doctors advice or can cause severe side effects
Homeopathy medicine should be taken only after homeopathy doctors advice or can cause severe side effects
About Paralysis Course

3 To 6 Month AVG Course
होम्योपैथी एक धीमी लेकिन स्थायी उपचार प्रक्रिया है — जितनी पुरानी बीमारी, उतना अधिक समय लग सकता है। मरीज की रिकवरी उसकी इम्यूनिटी सिस्टम की मजबूती पर भी निर्भर करती है।

98% Success Rate
क्या आप भी एलर्जी से परेशान होकर सिट्रिज़िन या अन्य गोलियों और इंजेक्शनों के सहारे दिन गुजार रहे हैं? क्या एलर्जी के कारण आप चैन की नींद नहीं ले पा रहे हैं? क्या आपने भी मान लिया है कि आपकी एलर्जी कभी ठीक नहीं हो सकती? अगर हाँ, तो यह कोर्स आपके लिए एक नई उम्मीद है — एक ऐसा समाधान जो जड़ों से इलाज करता है, न कि सिर्फ लक्षणों को दबाता है।
No Hidden Charges
Fix Charges - ₹199 For First Time Consultation Fee+ ₹800 Medicine Charges (Delivery Charges Apply)

3 Layer Advance Homeopathy* Medicine Kit
साधारण होम्योपैथिक दवाएं बीमारी से अस्थायी राहत तो देती हैं, लेकिन उसे पूरी तरह जड़ से खत्म नहीं कर पातीं। वहीं, Bhomeo की एडवांस होम्योपैथी पद्धति बीमारी को जड़ से समाप्त करती है और उसके बार-बार लौटने की संभावना को भी रोकती है।

हमारा प्लान कैसे काम करता है ?
घर बैठे ऑनलाइन इलाज की प्रक्रिया

Book Appointment
✅ नीचे दिए गए Book Now बटन पर क्लिक करें और ₹199 का भुगतान करें। 📞 भुगतान के बाद, डॉक्टर की अपॉइंटमेंट टाइमिंग आपको आपके WhatsApp नंबर पर भेज दी जाएगी।

Expect a Doctor’s Call on Your Mobile Soon!
📞 Bhomeo के एक्सपर्ट डॉक्टर का कॉल आपके मोबाइल पर तय समय ⏰ पर आएगा। 🏠 इसके बाद हमारी टीम WhatsApp के माध्यम से आपका पता वेरीफाई करेगी ताकि आपका ट्रीटमेंट जल्दी शुरू हो सके!

Fast Home Delivery
🚚 आपकी एडवांस होम्योपैथी दवाइयाँ 💊 4 से 6 वर्किंग डेज में आपके पते 📍 पर पहुँच जाएगी। व्हाट्सएप पर ट्रैकिंग ID 📲 दी जाएगी ताकि आप डिलीवरी ट्रैक 📦 कर सकें। दवाई के चार्ज ₹800 💸, प्रति 15 दिन के लिए। (*डिलीवरी चार्ज एक्सट्रा, COD उपलब्ध 🚚)
Advance Bhomeo Homeopathy अब आपके घर पे
First Time Consultation Fee: ₹199/- Only
💵 Cash on Delivery (COD) या Prepaid दोनों विकल्प उपलब्ध हैं।
💊 15 Days Medical Charges: ₹800/-

हमारे Treatment की ख़ास बात
Bhomeo Advance Homeopathy
जानिए हमारे इलाज की सबसे खास बातें जो हमें बाकी सभी से अलग बनाती हैं।

01
Root Cause Analysis
Right diagnosis + बिमारी का जड से इलाज + व्यक्ती & प्रकृती & मानसिकता & बिमारी = हर बिमारी का सही कारण जानकर परमनंट इलाज.

02
Holistic Remedy
बिमारी + शरीर + मन और भावना – तीनों स्तरों पर काम करने वाली दवा।

03
Targeted Symptom Relief
Immediate comfort, long-term healing

04
100 % Personalised Treatment kit
🩺 हर इंसान अलग, इसलिए हर इलाज भी अलग — आपकी खास दवाओं की पर्सनल किट। 🚚 डिलीवरी सीधे आपके घर पर!

अब चिंता की कोई बात नहीं
पैरालिसिस के लक्षण और कारण
पैरालिसिस (Paralysis) के लक्षणों में चेहरे के एक भाग की मांसपेशियों में कमजोरी, दर्द और असामान्य शारीरिक गतिविधियाँ शामिल हो सकती हैं। बेल्स पाल्सी (Bell's Palsy) में अचानक चेहरे पर लकवे के लक्षण दिखाई देते हैं, जिनका इलाज फिजियोथेरेपी और विशेष उपचार विधियों से संभव है। इस स्थिति में Bell's Palsy विशेषज्ञ डॉक्टर की सलाह से बेहतर परिणाम मिल सकते हैं। वहीं, सेरेब्रल पाल्सी (Cerebral Palsy) में मांसपेशियों की कमजोरी और चलने-फिरने में असामान्यता देखने को मिलती है, जिसे फेशियल पैरालिसिस ट्रीटमेंट और नियमित फिजियोथेरेपी द्वारा नियंत्रित किया जा सकता है। इन दोनों ही अवस्थाओं में समय पर और उचित इलाज से रोगी के जीवन की गुणवत्ता में उल्लेखनीय सुधार किया जा सकता है।

महत्वपूर्ण
पैरालिसिस का इलाज
bhomeo.in पर पैरालिसिस (Paralysis) का प्रभावी होम्योपैथिक इलाज उपलब्ध है, जिसमें विशेष रूप से Bell's Palsy के लिए थेरैपी शामिल है। अनुभवी Bell's Palsy डॉक्टर की निगरानी में रोगियों को उनकी स्थिति के अनुसार व्यक्तिगत उपचार योजना प्रदान की जाती है, जो चेहरे की मांसपेशियों की कमजोरी और लकवे को सुधारने में सहायक होती है। Cerebral Palsy से पीड़ित मरीजों के लिए भी यहां विशेष फिजियोथेरेपी और होम्योपैथिक चिकित्सा दी जाती है, जो मांसपेशियों की ताकत और समन्वय को बेहतर बनाती है। Facial paralysis treatment के तहत समग्र देखभाल और प्राकृतिक होम्योपैथिक उपचार से जीवन की गुणवत्ता में उल्लेखनीय सुधार संभव है।

अभी सम्पर्क करे
Homeopathy vs BHOMEO Homeopathy
Bhomeo.in होम्योपैथी में बीमारी के लक्षणों के आधार पर सर्वश्रेष्ठ दवाइयाँ दी जाती हैं, जो शरीर की रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता को बढ़ाती हैं। इसमें एंटी-मियास्मैटिक दवाओं का उपयोग किया जाता है और मरीज की विशिष्ट स्थिति को ध्यान में रखकर व्यक्तिगत उपचार किट प्रदान की जाती है। यह पद्धति लक्षणों को तेजी से नियंत्रित करने और शीघ्र सुधार सुनिश्चित करने में प्रभावी है। पारंपरिक होम्योपैथी की तुलना में, बिहोमियो एडवांस होम्योपैथी की विस्तृत और विज्ञान-आधारित तकनीकें अधिक सटीक, सुरक्षित और तेज परिणाम देती हैं, जिससे मरीजों को जल्दी राहत मिलती है।
Online or Offline
आपके स्वास्थ्य के लिए कौन सा बेहतर है?
bhomeo.in के सभी केंद्रों पर एकसमान उन्नत और शोध-आधारित होम्योपैथिक उपचार प्रदान किया जाता है। bhomeo.in आपके बताए गए लक्षणों पर आधारित उपचार करता है। आप घर बैठे फोन पर डॉक्टर से बात कर अपनी बीमारी के लक्षण बता सकते हैं या हमारे केंद्र पर आकर डॉक्टर को दिखा सकते हैं—दोनों ही मामलों में आपको वही प्रभावी दवाइयाँ मिलेंगी। यदि कोई रिपोर्ट भेजनी हो, तो आप इसे हमारे WhatsApp पर भेज सकते हैं।
Online इलाज =Offline इलाज
Same Care. Same Cure. Same Cost — हर बार, हर जगह।

आपके कुछ सामान्य सवाल
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
bhomeo.in एक ऑनलाइन प्लेटफॉर्म है जो होम्योपैथिक उपचार के लिए व्यक्तिगत परामर्श, उपचार योजना, और स्वास्थ्य संबंधी सुझाव प्रदान करता है। यह विभिन्न शारीरिक और मानसिक समस्याओं के लिए विशेषज्ञ सहायता उपलब्ध कराता है।
हां, bhomeo.in पर आप योग्य और अनुभवी होम्योपैथिक डॉक्टरों से ऑनलाइन परामर्श ले सकते हैं। वे आपकी समस्याओं का गहराई से मूल्यांकन करके व्यक्तिगत उपचार योजना प्रदान करते हैं।
हां, bhomeo.in सभी आयु वर्ग के व्यक्तियों के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार प्रदान करता है, चाहे वे बच्चे हों, युवा हों, या बुजुर्ग। यह सुरक्षित और प्रभावी उपचार के लिए जाना जाता है।
होम्योपैथिक उपचार प्राकृतिक और सुरक्षित माने जाते हैं। bhomeo.in के विशेषज्ञों द्वारा दी जाने वाली दवाइयां आमतौर पर दुष्प्रभाव मुक्त होती हैं, लेकिन उपचार से पहले आपकी पूरी स्वास्थ्य स्थिति का विश्लेषण किया जाता है।
आप bhomeo.in पर अपनी समस्या के विवरण के साथ एक अकाउंट बनाकर परामर्श का समय तय कर सकते हैं। डॉक्टर आपकी स्थिति का मूल्यांकन करेंगे और आपको व्यक्तिगत उपचार योजना प्रदान करेंगे।
